浅析计算GMAC和GFLOPS
GMAC 代表“Giga Multiply-Add Operations per Second”(每秒千兆乘法累加运算),是用于衡量深度学习模型计算效率的指标。该指标用每秒十亿个乘加运算的形式表示模型的计算速度。

乘法累加 (MAC) 运算是许多数学计算中的基本运算,包括矩阵乘法、卷积和深度学习中常用的其他张量运算。每个 MAC 操作都涉及将两个数字相乘并将结果添加到累加器。
可以使用以下公式计算 GMAC 指标:
<code>GMAC =(乘法累加运算次数)/(10⁹)</code>
乘加运算的数量通常通过分析网络架构和模型参数的维度来确定,例如权重和偏差。
通过 GMAC 指标,研究人员和从业者可以就模型选择、硬件要求和优化策略做出明智的决策,以实现高效且有效的深度学习计算。

GFLOPS是计算机系统或特定运算计算性能的衡量指标,代表每秒可执行十亿次浮点运算。它是每秒钟浮点运算的数量,用十亿 (giga) 表示。
浮点运算是指进行以 IEEE 754 浮点格式表示的实数进行算术计算。这些运算通常包括加法、减法、乘法、除法和其他数学运算。
GFLOPS 通常用于高性能计算 (HPC) 和基准测试,特别是在需要繁重计算任务的领域,例如科学模拟、数据分析和深度学习。
计算 GFLOPS公式如下:
<code>GFLOPS =(浮点运算次数)/(以秒为单位的运行时间)/ (10⁹)</code>
GFLOPS是一项有效的测量不同计算机系统、处理器或特定操作的计算能力的指标。它有助于评估执行浮点计算的硬件或算法的速度和效率。GFLOPS 是衡量理论峰值性能的指标,可能无法反映实际场景中实现的实际性能,因为它没有考虑内存访问、并行化和其他系统限制等因素。
GMAC 和 GFLOPS 之间的关系
<code>1 GFLOP = 2 GMAC</code>
如果我们想计算这两个指标,手动写代码的话会比较麻烦,但是Python已经有现成的库让我们使用:
ptflops 库就可以计算 GMAC 和 GFLOPs
<code>pip install ptflops</code>
使用也非常简单:
<code>import torchvision.models as models import torch from ptflops import get_model_complexity_info import re #Model thats already available net = models.densenet161() macs, params = get_model_complexity_info(net, (3, 224, 224), as_strings=True, print_per_layer_stat=True, verbose=True) # Extract the numerical value flops = eval(re.findall(r'([\d.]+)', macs)[0])*2 # Extract the unit flops_unit = re.findall(r'([A-Za-z]+)', macs)[0][0] print('Computational complexity: {:<8}'.format(macs)) print('Computational complexity: {} {}Flops'.format(flops, flops_unit)) print('Number of parameters: {:<8}'.format(params))</code>结果如下:
<code>Computational complexity: 7.82 GMac Computational complexity: 15.64 GFlops Number of parameters: 28.68 M</code>
我们可以自定义一个模型来看看结果是否正确:
<code>import os import torch from torch import nn class NeuralNetwork(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.flatten = nn.Flatten() self.linear_relu_stack = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(28*28, 512), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(512, 512), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(512, 10),) def forward(self, x): x = self.flatten(x) logits = self.linear_relu_stack(x) return logits custom_net = NeuralNetwork() macs, params = get_model_complexity_info(custom_net, (28, 28), as_strings=True, print_per_layer_stat=True, verbose=True) # Extract the numerical value flops = eval(re.findall(r'([\d.]+)', macs)[0])*2 # Extract the unit flops_unit = re.findall(r'([A-Za-z]+)', macs)[0][0] print('Computational complexity: {:<8}'.format(macs)) print('Computational complexity: {} {}Flops'.format(flops, flops_unit)) print('Number of parameters: {:<8}'.format(params))</code>结果如下:
<code>Computational complexity: 670.73 KMac Computational complexity: 1341.46 KFlops Number of parameters: 669.71 k</code>
为了方便演示,我们只编写全连接层代码来手动计算GMAC。遍历模型权重参数并计算乘法和加法操作数量的形状取决于权重参数,这是计算GMAC的关键。计算GMAC所需的全连接层权重的公式为2 x (输入维度 x 输出维度) 。总的GMAC值是通过将每个线性层的权重参数的形状相乘并累加而得出的,这一过程基于模型的结构。
<code>import torch import torch.nn as nn def compute_gmac(model): gmac_count = 0 for param in model.parameters(): shape = param.shape if len(shape) == 2:# 全连接层的权重 gmac_count += shape[0] * shape[1] * 2 gmac_count = gmac_count / 1e9# 转换为十亿为单位 return gmac_count</code>
根据上面给定的模型,计算GMAC的结果如下:
<code>0.66972288</code>
由于GMAC的结果以十亿为单位,因此与我们上面使用类库计算的结果相差不大。最后再说一下,计算卷积的GMAC稍微有些复杂,公式为 ((输入通道 x 卷积核高度 x 卷积核宽度) x 输出通道) x 2,这里给一个简单的代码,不一定完全正确,供参考
<code>def compute_gmac(model): gmac_count = 0 for param in model.parameters(): shape = param.shape if len(shape) == 2:# 全连接层的权重 gmac_count += shape[0] * shape[1] * 2 elif len(shape) == 4:# 卷积层的权重 gmac_count += shape[0] * shape[1] * shape[2] * shape[3] * 2 gmac_count = gmac_count / 1e9# 转换为十亿为单位 return gmac_count</code>
以上是浅析计算GMAC和GFLOPS的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 Python中使用BERT进行情感分析的方法及步骤
Jan 22, 2024 pm 04:24 PM
Python中使用BERT进行情感分析的方法及步骤
Jan 22, 2024 pm 04:24 PM
BERT是由Google在2018年提出的一种预训练的深度学习语言模型。全称为BidirectionalEncoderRepresentationsfromTransformers,它基于Transformer架构,具有双向编码的特点。相比于传统的单向编码模型,BERT在处理文本时能够同时考虑上下文的信息,因此在自然语言处理任务中表现出色。它的双向性使得BERT能够更好地理解句子中的语义关系,从而提高了模型的表达能力。通过预训练和微调的方法,BERT可以用于各种自然语言处理任务,如情感分析、命名
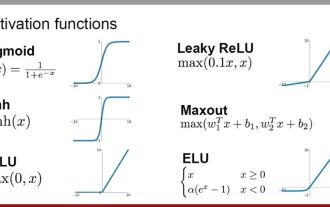 常用的AI激活函数解析:Sigmoid、Tanh、ReLU和Softmax的深度学习实践
Dec 28, 2023 pm 11:35 PM
常用的AI激活函数解析:Sigmoid、Tanh、ReLU和Softmax的深度学习实践
Dec 28, 2023 pm 11:35 PM
激活函数在深度学习中扮演着至关重要的角色,它们能够为神经网络引入非线性特性,使得网络能够更好地学习和模拟复杂的输入输出关系。正确选择和使用激活函数对于神经网络的性能和训练效果有着重要的影响本文将介绍四种常用的激活函数:Sigmoid、Tanh、ReLU和Softmax,从简介、使用场景、优点、缺点和优化方案五个维度进行探讨,为您提供关于激活函数的全面理解。1、Sigmoid函数SIgmoid函数公式简介:Sigmoid函数是一种常用的非线性函数,可以将任何实数映射到0到1之间。它通常用于将不归一
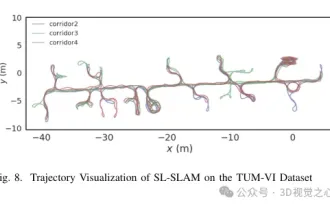 超越ORB-SLAM3!SL-SLAM:低光、严重抖动和弱纹理场景全搞定
May 30, 2024 am 09:35 AM
超越ORB-SLAM3!SL-SLAM:低光、严重抖动和弱纹理场景全搞定
May 30, 2024 am 09:35 AM
写在前面今天我们探讨下深度学习技术如何改善在复杂环境中基于视觉的SLAM(同时定位与地图构建)性能。通过将深度特征提取和深度匹配方法相结合,这里介绍了一种多功能的混合视觉SLAM系统,旨在提高在诸如低光条件、动态光照、弱纹理区域和严重抖动等挑战性场景中的适应性。我们的系统支持多种模式,包括拓展单目、立体、单目-惯性以及立体-惯性配置。除此之外,还分析了如何将视觉SLAM与深度学习方法相结合,以启发其他研究。通过在公共数据集和自采样数据上的广泛实验,展示了SL-SLAM在定位精度和跟踪鲁棒性方面优
 潜藏空间嵌入:解释与示范
Jan 22, 2024 pm 05:30 PM
潜藏空间嵌入:解释与示范
Jan 22, 2024 pm 05:30 PM
潜在空间嵌入(LatentSpaceEmbedding)是将高维数据映射到低维空间的过程。在机器学习和深度学习领域中,潜在空间嵌入通常是通过神经网络模型将高维输入数据映射为一组低维向量表示,这组向量通常被称为“潜在向量”或“潜在编码”。潜在空间嵌入的目的是捕捉数据中的重要特征,并将其表示为更简洁和可理解的形式。通过潜在空间嵌入,我们可以在低维空间中对数据进行可视化、分类、聚类等操作,从而更好地理解和利用数据。潜在空间嵌入在许多领域中都有广泛的应用,如图像生成、特征提取、降维等。潜在空间嵌入的主要
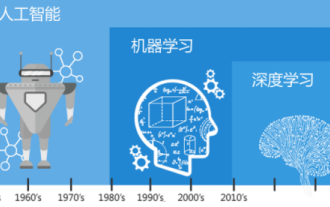 一文搞懂:AI、机器学习与深度学习的联系与区别
Mar 02, 2024 am 11:19 AM
一文搞懂:AI、机器学习与深度学习的联系与区别
Mar 02, 2024 am 11:19 AM
在当今科技日新月异的浪潮中,人工智能(ArtificialIntelligence,AI)、机器学习(MachineLearning,ML)与深度学习(DeepLearning,DL)如同璀璨星辰,引领着信息技术的新浪潮。这三个词汇频繁出现在各种前沿讨论和实际应用中,但对于许多初涉此领域的探索者来说,它们的具体含义及相互之间的内在联系可能仍笼罩着一层神秘面纱。那让我们先来看看这张图。可以看出,深度学习、机器学习和人工智能之间存在着紧密的关联和递进关系。深度学习是机器学习的一个特定领域,而机器学习
 超强!深度学习Top10算法!
Mar 15, 2024 pm 03:46 PM
超强!深度学习Top10算法!
Mar 15, 2024 pm 03:46 PM
自2006年深度学习概念被提出以来,20年快过去了,深度学习作为人工智能领域的一场革命,已经催生了许多具有影响力的算法。那么,你所认为深度学习的top10算法有哪些呢?以下是我心目中深度学习的顶尖算法,它们在创新性、应用价值和影响力方面都占据重要地位。1、深度神经网络(DNN)背景:深度神经网络(DNN)也叫多层感知机,是最普遍的深度学习算法,发明之初由于算力瓶颈而饱受质疑,直到近些年算力、数据的爆发才迎来突破。DNN是一种神经网络模型,它包含多个隐藏层。在该模型中,每一层将输入传递给下一层,并
 使用CNN和Transformer混合模型以提升性能的方法
Jan 24, 2024 am 10:33 AM
使用CNN和Transformer混合模型以提升性能的方法
Jan 24, 2024 am 10:33 AM
卷积神经网络(CNN)和Transformer是两种不同的深度学习模型,它们在不同的任务上都展现出了出色的表现。CNN主要用于计算机视觉任务,如图像分类、目标检测和图像分割等。它通过卷积操作在图像上提取局部特征,并通过池化操作进行特征降维和空间不变性。相比之下,Transformer主要用于自然语言处理(NLP)任务,如机器翻译、文本分类和语音识别等。它使用自注意力机制来建模序列中的依赖关系,避免了传统的循环神经网络中的顺序计算。尽管这两种模型用于不同的任务,但它们在序列建模方面有相似之处,因此
 改进的RMSprop算法
Jan 22, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
改进的RMSprop算法
Jan 22, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
RMSprop是一种广泛使用的优化器,用于更新神经网络的权重。它是由GeoffreyHinton等人在2012年提出的,并且是Adam优化器的前身。RMSprop优化器的出现主要是为了解决SGD梯度下降算法中遇到的一些问题,例如梯度消失和梯度爆炸。通过使用RMSprop优化器,可以有效地调整学习速率,并且自适应地更新权重,从而提高深度学习模型的训练效果。RMSprop优化器的核心思想是对梯度进行加权平均,以使不同时间步的梯度对权重的更新产生不同的影响。具体而言,RMSprop会计算每个参数的平方






