不使用乘法、除法和取模运算符来进行两个整数的除法

在这个问题中,我们只需要将两个整数相除,而不需要使用乘法、除法和取模运算符。尽管我们可以使用加法、乘法或位操作。
问题陈述指出我们将得到两个整数 x 和 y。在不使用乘法、除法或取模运算符的情况下,我们需要确定 x 除以 y 后的商。
示例
输入:x=15,y=5
输出:3
输入:x=10,y=4
输出:2
输入:x=-20,y=3
输出:-6
方法
方法1(使用简单的数学)
在这种方法中,我们将使用一个简单的数学算法。下面是我们要遵循的步骤的分步说明 -
我们将从被除数(即 x)中不断减去除数(即 y),直到 x 大于或等于 y。
当 y 大于 x 时,即除数大于被除数,被除数变为余数,减法次数变为商。
将减法执行的次数存储在变量中并返回它,这是我们想要的输出。
示例
下面是上述算法的 C++ 实现 &minnus;
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long division(long long a,long long b) // where a is dividend and b is divisor
{
long long sign=1;
if((a<0) ^( b<0)) // - ^ - = +,+ ^ - = - , - ^ + = - , + ^ + = +
{
sign=-1;
}
long long m=abs(a);
long long n=abs(b);
long long count=0; // for storing the quotient
while(m>=n){
m=m-n;
count++;
}
if(sign==-1) // when sign is negative
{
count=-count;
}
return count;
}
int main(){
long long a=-21474;
long long b=2;
long long val=division(a,b);
cout<<val<<endl;
return 0;
}
输出
-10737
时间复杂度:O(a/b)
空间复杂度:O(1)
方法 2(使用位操作)
由于任何数字都可以用 0 或 1 的形式表示,因此可以使用移位运算符以二进制形式表示商。
使用 for 循环迭代除数从 31 到 1 的位位置。
找到除数即 b<
验证下一个位置时,将结果添加到 temp 变量中,以确保 temp+(b<
每次通过计算商来更新商OR 1<
更新相应符号后返回商。
示例
下面是上述方法的 C++ 实现 -
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long division(long long a,long long b) // where a is dividend and b is divisor
{
long long sign=1;
if((a<0) ^( b<0)) // - ^ - = +,+ ^ - = - , - ^ + = - , + ^ + = +
{
sign=-1;
}
long long m=abs(a);
long long n=abs(b);
long long count=0; // for storing the quotient
long long temp=0;
for (int j = 31; j >= 0; --j){
if (temp + (n << j) <= m){
temp += n << j;
count |= 1L << j;
}
}
if(sign==-1) // when sign is negative
{
count=-count;
}
return count;
}
int main(){
long long a=49;
long long b=5;
long long val=division(a,b);
cout<<val<<endl;
a=-18,b=5;
cout<<division(a,b);
return 0;
}
输出
9 -3
时间复杂度:O(log(a))
空间复杂度:O(1),因为它不使用额外的空间。
方法 3(使用对数函数)
在这种方法中,我们将使用一个简单的对数函数来计算商。
众所周知,
$$mathrm{In(frac{a}{b}):=:In(a):-:In(b)}$$
可以进一步修改为
$$mathrm{frac{a}{b}:=:e^{(In(a):-:In(b))}}$$
因此,这是使用这种有效方法解决给定问题的基本思想。
下面是我们将要遵循的方法的分步说明 -
如果其中一个(即被除数或除数)为 0,我们将返回 0。
现在,我们将使用异或函数 (XOR) 检查符号,以将符号存储在变量中。
如果除数为 1,则直接返回被除数。
现在,声明一个变量并使用 exp< 将等于 $mathrm{e^{(In(a):-:In(b))}}$ 的值存储在其中/b> 函数和 log 函数。
Log 和 exp 是 C++ 中的内置函数。 Log 函数返回输入数字的自然对数值,exp 返回等于 e 加上输入值的值。
示例
下面是上述方法的 C++ 实现 -
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long int divide(long long int a,long long int b){
long long int sign=1;
if(a==0||b==0) // when a is zero or b is zero
{
return 0;
}
if((a>0) ^ (b>0)) // - ^ - = +,+ ^ - = - , - ^ + = - , + ^ + = +
{
sign=-1;
}
if(b==1) // when b is 1 then it will return a example 51/1 = 51
{
sign==-1?-a:a;
return a;
}
long long int m=abs(a);
long long int n=abs(b);
//log function return the logarithmic value of the entered value with base e i.e. natural log of the entered value
//exp function return the value equal to e^(entered value)
long long int ans =exp(log(m) - log(n)) + 0.0000000001;
// if it gives the value in decimal we will add from 0.0000000001 to account for accuracy errors
if(sign==-1) // when sign is negative return the negative ans
{
return -ans;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
long long int ans=divide(47,-9);
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
输出
-5
时间复杂度:O(1),,因为执行该操作需要恒定的时间。
空间复杂度:O(1),因为它不使用额外的空间。
结论
在本文中,我们学习在不使用乘法、除法或取模运算符的情况下将两个整数相除。我们学会了用不同的方法以不同的效率解决问题。他们使用简单的数学、位操作和对数函数。其中,使用对数函数是最有效的方法,因为它的时间复杂度为 O(1),是所有方法中最小的。
我希望这篇文章可以帮助您解决有关该主题的所有概念。
以上是不使用乘法、除法和取模运算符来进行两个整数的除法的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

热门话题
 不使用乘法、除法和取模运算符来进行两个整数的除法
Sep 21, 2023 pm 12:41 PM
不使用乘法、除法和取模运算符来进行两个整数的除法
Sep 21, 2023 pm 12:41 PM
在这个问题中,我们只需要将两个整数相除,而不需要使用乘法、除法和取模运算符。尽管我们可以使用加法、乘法或位操作。问题陈述指出我们将得到两个整数x和y。在不使用乘法、除法或取模运算符的情况下,我们需要确定x除以y后的商。示例输入:x=15,y=5输出:3输入:x=10,y=4输出:2输入:x=-20,y=3输出:-6方法方法1(使用简单的数学)在这种方法中,我们将使用一个简单的数学算法。下面是我们要遵循的步骤的分步说明-我们将从被除数(即x)中不断减去除数(即y),直到x大于或等于y。当y大于x时
 Oracle数据库运算技巧:减法操作详解
Mar 02, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Oracle数据库运算技巧:减法操作详解
Mar 02, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Oracle数据库作为一种功能强大的关系型数据库管理系统,提供了丰富的运算操作来满足用户的需求。在日常的数据库操作中,减法操作是一个常见且重要的运算,它能够帮助我们实现数据的减法运算,从而得到我们所需的结果。本文将详细讨论Oracle数据库中减法操作的相关技巧,并给出具体的代码示例,帮助读者更好地理解和运用这一功能。1.减法操作的基本概念在Oracle数据
 PHP 精准除法取整数结果
Apr 09, 2024 pm 01:09 PM
PHP 精准除法取整数结果
Apr 09, 2024 pm 01:09 PM
PHP中除法运算符(/)默认进行浮点除法,若需取商的整数结果,可使用以下方法:floor()函数:向下舍入整数(例:floor(10.5)=10)ceil()函数:向上舍入整数(例:ceil(10.5)=11)截断运算符(//):截断为整数取模运算符(%):检查余数是否为0以判断结果是否为整数
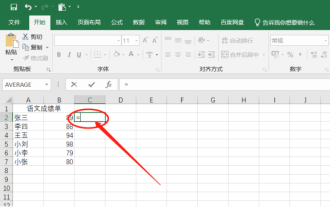 Excel怎么做减法
Mar 20, 2024 pm 02:46 PM
Excel怎么做减法
Mar 20, 2024 pm 02:46 PM
Excel是我们日常办公中必不可少的一个办公软件,那么对于一些初次学习Excel的人来说总会遇到一些小问题,就比如Excel怎么做减法这一问题,今天我就来跟小伙伴们分享这一操作步骤,具体的操作步骤就在下方,小伙伴们快来认真的看一看吧!1.首先,打开Excel数据表,Excel想要做减法是通过公式来实现的,而公式一般都是由等号引导的,故在需要做减法的单元格中,先输入=,(如下图红色圈出部分所示)。2.然后,点击被减数所在的单元格,就会自动在公式中补充上该单元格的名字,(如下图红色圈出部分所示)。3
 探究Python运算符的含义和应用:加、减、乘、除
Jan 20, 2024 am 09:21 AM
探究Python运算符的含义和应用:加、减、乘、除
Jan 20, 2024 am 09:21 AM
深入理解Python运算符:加法、减法、乘法、除法及其含义,需要具体代码示例在Python编程语言中,运算符是进行各种数学操作的重要工具之一。其中,加法、减法、乘法和除法是最常见的运算符,本文将深入探讨这些运算符的含义及其在Python中的使用方法。加法运算符(+)加法运算符用于将两个数字相加,也可以用于连接两个字符串。x=5y=3result
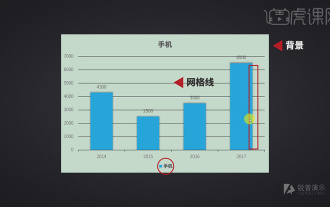 PPT如何制作减法设计美化图表
Mar 20, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
PPT如何制作减法设计美化图表
Mar 20, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
1.图表的基本美化操作空间小,将干扰的展示元素去掉。干扰数据的元素有背景、网格线、图例,可以将其删除美化以及阴影进行柔化。2.进入【PPT】,【打开】图表,点击【图表】,选择【+】,将其取消【勾选】,具体如图示。3.【右键】设置数据系列格式,点击【填充】,勾选【无填充】。点击【数据列】,点击【阴影】去除阴影,选择【外框】,将【文字】颜色白色。4.点击【刻度】,选择【刻度线】,调整【主题类型】无,【颜色】白色,具体如图示。5.将需要删除的地方删除,使表格变得清爽,设计时不要一味的添加东西,适当的做
 使用pthread在C/C++中实现矩阵的加法和减法
Aug 28, 2023 am 09:05 AM
使用pthread在C/C++中实现矩阵的加法和减法
Aug 28, 2023 am 09:05 AM
这里我们将看到如何使用多线程环境执行矩阵加法和减法。pthread用于在C或C++中同时执行多个线程。有两个矩阵A和B。每个矩阵的阶数为(mxn)。每个线程将获取每一行,并执行加法或减法。因此,对于m行,有m个不同的线程。示例#include<iostream>#include<pthread.h>#include<cstdlib>#include<cstdint>#defineCORE3#defineMAX3usingnamespacestd;i
 为什么PHP中的8除以-3的结果为0?
Jan 26, 2024 am 10:36 AM
为什么PHP中的8除以-3的结果为0?
Jan 26, 2024 am 10:36 AM
PHP8%-3为何会等于0?在PHP编程中,有时候我们会遇到一些奇怪而又令人困惑的问题。一个特别有趣的问题就是,为什么PHP中的表达式8%-3会等于0?要回答这个问题,首先我们需要了解PHP中的模运算(取余运算)。模运算是一种数学运算,用于计算一个数除以另一个数的余数。在PHP中,用百分号(%)表示模运算。在数学中,当一个数除以另一个数的余数为0时,我们说这






