Android 热修复 Tinker 源码分析
tinker有个非常大的亮点就是自研发了一套dex diff、patch相关算法。本篇文章主要目的就是分析该算法。当然值得注意的是,分析的前提就是需要对dex文件的格式要有一定的认识,否则的话可能会一脸懵逼态。
所以,本文会先对dex文件格式做一个简单的分析,也会做一些简单的实验,最后进入到dex diff,patch算法部分。
首先简单了解下Dex文件,大家在反编译的时候,都清楚apk中会包含一个或者多个*.dex文件,该文件中存储了我们编写的代码,一般情况下我们还会通过工具转化为jar,然后通过一些工具反编译查看。
jar文件大家应该都清楚,类似于class文件的压缩包,一般情况下,我们直接解压就可以看到一个个class文件。而dex文件我们无法通过解压获取内部的一个个class文件,说明dex文件拥有自己特定的格式:
dex对Java类文件重新排列,将所有JAVA类文件中的常量池分解,消除其中的冗余信息,重新组合形成一个常量池,所有的类文件共享同一个常量池,使得相同的字符串、常量在DEX文件中只出现一次,从而减小了文件的体积。
接下来我们看看dex文件的内部结构到底是什么样子。
分析一个文件的组成,最好自己编写一个最简单的dex文件来分析。
首先我们编写一个类Hello.java:
public class Hello{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("hello dex!");
}
}然后进行编译:
javac -source 1.7 -target 1.7 Hello.java
最后通过dx工作将其转化为dex文件:
dx --dex --output=Hello.dex Hello.class
dx路径在Android-sdk/build-tools/版本号/dx下,如果无法识别dx命令,记得将该路径放到path下,或者使用绝对路径。
这样我们就得到了一个非常简单的dex文件。
首先展示一张dex文件的大致的内部结构图:
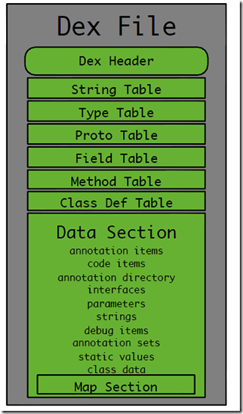
当然,单纯从一张图来说明肯定是远远不够的,因为我们后续要研究diff,patch算法,理论上我们应该要知道更多的细节,甚至要细致到:一个dex文件的每个字节表示的是什么内容。
对于一个类似于二进制的文件,最好的办法肯定不是靠记忆,好在有这么一个软件可以帮助我们的分析:
- 软件名称:010 Editor
下载完成安装后,打开我们的dex文件,会引导你安装dex文件的解析模板。
最终打开效果图如下:
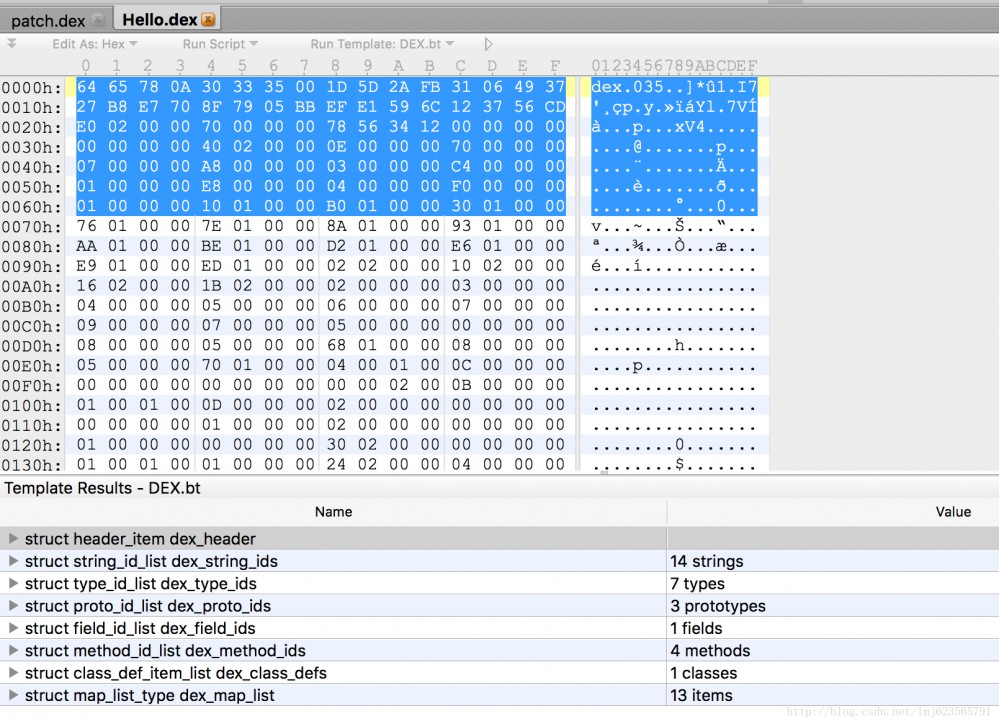
上面部分代表了dex文件的内容(16进制的方式展示),下面部分展示了dex文件的各个区域,你可以通过点击下面部分,来查看其对应的内容区域以及内容。
当然这里也非常建议,阅读一些专门的文章来加深对dex文件的理解:
- DEX文件格式分析
- Android逆向之旅—解析编译之后的Dex文件格式
本文也仅会对dex文件做简单的格式分析。
dex_header
首先我们队dex_header做一个大致的分析,header中包含如下字段:
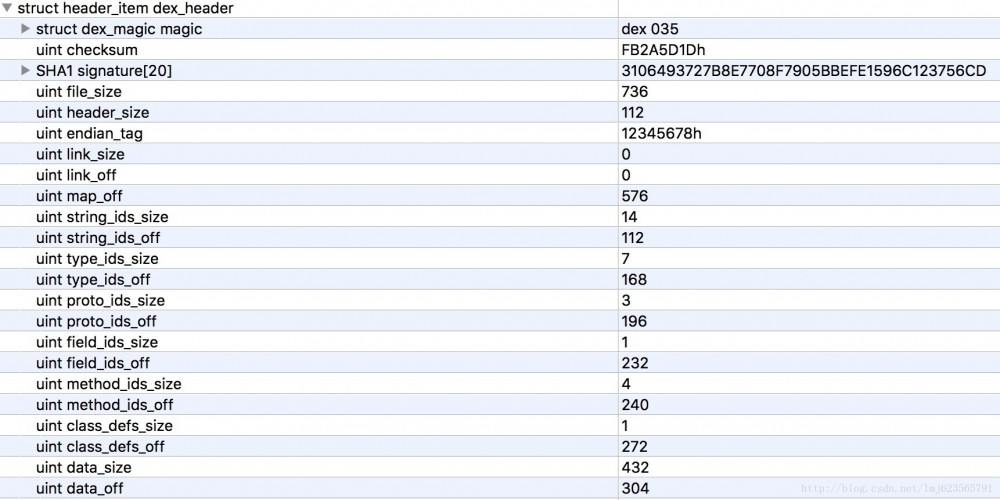
首先我们猜测下header的作用,可以看到起包含了一些校验相关的字段,和整个dex文件大致区块的分布(off都为偏移量)。
这样的好处就是,当虚拟机读取dex文件时,只需要读取出header部分,就可以知道dex文件的大致区块分布了;并且可以检验出该文件格式是否正确、文件是否被篡改等。
- 能够证明该文件是dex文件
- checksum和signature主要用于校验文件的完整性
- file_size为dex文件的大小
- head_size为头文件的大小
- endian_tag预设值为12345678,标识默认采用Little-Endian(自行搜索)。
剩下的几乎都是成对出现的size和off,大多代表各区块的包含的特定数据结构的数量和偏移量。例如:string_ids_off为112,指的是偏移量112开始为string_ids区域;string_ids_size为14,代表string_id_item的数量为14个。剩下的都类似就不介绍了。
结合010Editor可以看到各个区域包含的数据结构,以及对应的值,慢慢看就好了。
除了header还有个比较重要的部分是dex_map_list,首先看个图:
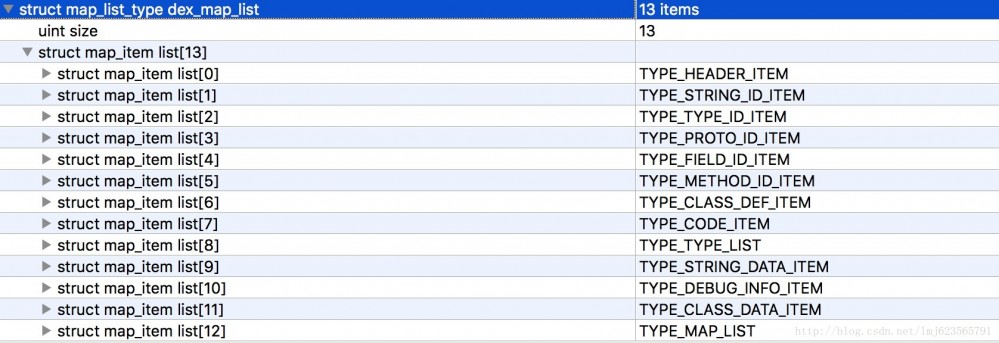
首先是map_item_list数量,接下来是每个map_item_list的描述。
map_item_list有什么用呢?
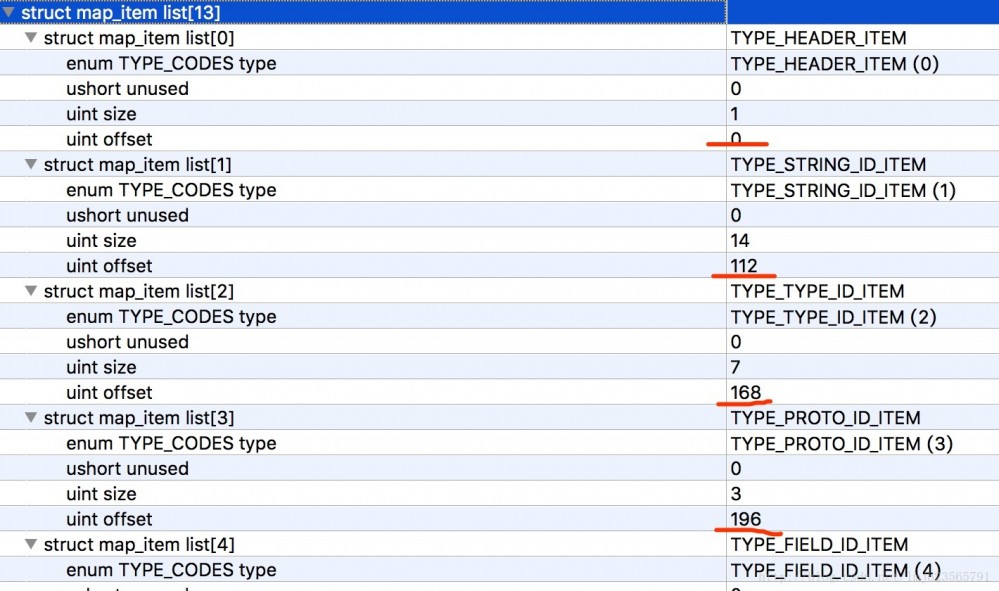
可以看到每个map_list_item包含一个枚举类型,一个2字节暂未使用的成员、一个size表明当前类型的个数,offset表明当前类型偏移量。
拿本例来说:
- 首先是TYPE_HEADER_ITEM类型,包含1个header(size=1),且偏移量为0。
- 接下来是TYPE_STRING_ID_ITEM,包含14个string_id_item(size=14),且偏移量为112(如果有印象,header的长度为112,紧跟着header)。
剩下的依次类推~~
这样的话,可以看出通过map_list,可以将一个完整的dex文件划分成固定的区域(本例为13),且知道每个区域的开始,以及该区域对应的数据格式的个数。
通过map_list找到各个区域的开始,每个区域都会对应特定的数据结构,通过010 Editor看就好了。
现在我们了解了dex的基本格式,接下来我们考虑下如何做dex diff 和 patch。
先要考虑的是我们有什么:
- old dex
- new dex
我们想要生成一个patch文件,该文件和old dex 通过patch算法还能生成new dex。
- 那么我们该如何做呢?
根据上文的分析,我们知道dex文件大致有3个部分(这里3个部分主要用于分析,勿较真):
- header
- 各个区域
- map list
header实际上是可以根据后面的数据确定其内容的,并且是定长112的;各个区域后面说;map list实际上可以做到定位到各个区域开始位置;
我们最终patch + old dex -> new dex;针对上述的3个部分,
- header我们可以不做处理,因为可以根据其他数据生成;
- map list这个东西,其实我们主要要的是各个区域的开始(offset)
- 知道了各个区域的offset后,在我们生成new dex的时候,我们就可以定位各个区域的开始和结束位置,那么只需要往各个区域写数据即可。
那么我们看看针对一个区域的diff,假设有个string区域,主要用于存储字符串:
old dex该区域的字符串有: Hello、World、zhy
new dex该区域的字符串有: Android、World、zhy
可以看出,针对该区域,我们删除了Hello,增加了Android。
那么patch中针对该区域可以如下记录:
“del Hello , add Android”(实际情况需要转化为二进制)。
想想应用中可以直接读取出old dex,即知道:
- 原来该区域包含:Hello、World、zhy
- patch中该区域包含:”del Hello , add Android”
那么,可以非常容易的计算出new dex中包含:
Android、World、zhy。
这样我们就完成了一个区域大致的diff和patch算法,其他各个区域的diff和patch和上述类似。
这样来看,是不是觉得这个diff和patch算法也没有那么的复杂,实际上tinker的做法与上述类似,实际情况可能要比上述描述要复杂一些,但是大体上是差不多的。
有了一个大致的算法概念之后,我们就可以去看源码了。
这里看代码实际上也是有技巧的,tinker的代码实际上蛮多的,往往你可以会陷在一堆的代码中。我们可以这么考虑,比如diff算法,输入参数为old dex 、new dex,输出为patch file。
那么肯定存在某个类,或者某个方法接受和输出上述参数。实际上该类为DexPatchGenerator:
diff的API使用代码为:
@Test
public void testDiff() throws IOException {
File oldFile = new File("Hello.dex");
File newFile = new File("Hello-World.dex");
File patchFile = new File("patch.dex");
DexPatchGenerator dexPatchGenerator
= new DexPatchGenerator(oldFile, newFile);
dexPatchGenerator.executeAndSaveTo(patchFile);
}代码在tinker-build的tinker-patch-lib下。
写一个单元测试或者main方法,上述几行代码就是diff算法。
所以查看代码时要有针对性,比如看diff算法,就找到diff算法的入口,不要在gradle plugin中去纠结。
public DexPatchGenerator(File oldDexFile, File newDexFile) throws IOException {
this(new Dex(oldDexFile), new Dex(newDexFile));
}将我们传入的dex文件转化为了Dex对象。
public Dex(File file) throws IOException {
// 删除了一堆代码
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
loadFrom(in, (int) file.length());
}
private void loadFrom(InputStream in, int initSize) throws IOException {
byte[] rawData = FileUtils.readStream(in, initSize);
this.data = ByteBuffer.wrap(rawData);
this.data.order(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN);
this.tableOfContents.readFrom(this);
}首先将我们的文件读取为byte[]数组(这里还是蛮耗费内存的),然后由ByteBuffer进行包装,并设置字节顺序为小端(这里说明ByteBuffer还是蛮方便的。然后通过readFrom方法为Dex对象的tableOfContents赋值。
#TableOfContents
public void readFrom(Dex dex) throws IOException {
readHeader(dex.openSection(header));
// special case, since mapList.byteCount is available only after
// computeSizesFromOffsets() was invoked, so here we can't use
// dex.openSection(mapList) to get dex section. Or
// an {@code java.nio.BufferUnderflowException} will be thrown.
readMap(dex.openSection(mapList.off));
computeSizesFromOffsets();
}在其内部执行了readHeader和readMap,上文我们大致分析了header和map list相关,实际上就是将这两个区域转化为一定的数据结构,读取然后存储到内存中。
首先看readHeader:
private void readHeader(Dex.Section headerIn) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
byte[] magic = headerIn.readByteArray(8);
int apiTarget = DexFormat.magicToApi(magic);
if (apiTarget != DexFormat.API_NO_EXTENDED_OPCODES) {
throw new DexException("Unexpected magic: " + Arrays.toString(magic));
}
checksum = headerIn.readInt();
signature = headerIn.readByteArray(20);
fileSize = headerIn.readInt();
int headerSize = headerIn.readInt();
if (headerSize != SizeOf.HEADER_ITEM) {
throw new DexException("Unexpected header: 0x" + Integer.toHexString(headerSize));
}
int endianTag = headerIn.readInt();
if (endianTag != DexFormat.ENDIAN_TAG) {
throw new DexException("Unexpected endian tag: 0x" + Integer.toHexString(endianTag));
}
linkSize = headerIn.readInt();
linkOff = headerIn.readInt();
mapList.off = headerIn.readInt();
if (mapList.off == 0) {
throw new DexException("Cannot merge dex files that do not contain a map");
}
stringIds.size = headerIn.readInt();
stringIds.off = headerIn.readInt();
typeIds.size = headerIn.readInt();
typeIds.off = headerIn.readInt();
protoIds.size = headerIn.readInt();
protoIds.off = headerIn.readInt();
fieldIds.size = headerIn.readInt();
fieldIds.off = headerIn.readInt();
methodIds.size = headerIn.readInt();
methodIds.off = headerIn.readInt();
classDefs.size = headerIn.readInt();
classDefs.off = headerIn.readInt();
dataSize = headerIn.readInt();
dataOff = headerIn.readInt();
}如果你现在打开着010 Editor,或者看一眼最前面的图,实际上就是将header中所有的字段定义出来,读取响应的字节并赋值。
接下来看readMap:
private void readMap(Dex.Section in) throws IOException {
int mapSize = in.readInt();
Section previous = null;
for (int i = 0; i < mapSize; i++) {
short type = in.readShort();
in.readShort(); // unused
Section section = getSection(type);
int size = in.readInt();
int offset = in.readInt();
section.size = size;
section.off = offset;
previous = section;
}
header.off = 0;
Arrays.sort(sections);
// Skip header section, since its offset must be zero.
for (int i = 1; i < sections.length; ++i) {
if (sections[i].off == Section.UNDEF_OFFSET) {
sections[i].off = sections[i - 1].off;
}
}
}这里注意,在读取header的时候,实际上已经读取除了map list区域的offset,并存储在mapList.off中。所以map list中实际上是从这个位置开始的。首先读取的就是map_list_item的个数,接下来读取的就是每个map_list_item对应的实际数据。
可以看到依次读取:type,unused,size,offset,如果你还有印象前面我们描述了map_list_item是与此对应的,对应的数据结构为TableContents.Section对象。
computeSizesFromOffsets()主要为section的byteCount(占据了多个字节)参数赋值。
到这里就完成了dex file 到 Dex对象的初始化。
有了两个Dex对象之后,就需要去做diff操作了。
继续回到源码:
public DexPatchGenerator(File oldDexFile, InputStream newDexStream) throws IOException {
this(new Dex(oldDexFile), new Dex(newDexStream));
}直接到两个Dex对象的构造函数:
public DexPatchGenerator(Dex oldDex, Dex newDex) {
this.oldDex = oldDex;
this.newDex = newDex;
SparseIndexMap oldToNewIndexMap = new SparseIndexMap();
SparseIndexMap oldToPatchedIndexMap = new SparseIndexMap();
SparseIndexMap newToPatchedIndexMap = new SparseIndexMap();
SparseIndexMap selfIndexMapForSkip = new SparseIndexMap();
additionalRemovingClassPatternSet = new HashSet<>();
this.stringDataSectionDiffAlg = new StringDataSectionDiffAlgorithm(
oldDex, newDex,
oldToNewIndexMap,
oldToPatchedIndexMap,
newToPatchedIndexMap,
selfIndexMapForSkip
);
this.typeIdSectionDiffAlg = ...
this.protoIdSectionDiffAlg = ...
this.fieldIdSectionDiffAlg = ...
this.methodIdSectionDiffAlg = ...
this.classDefSectionDiffAlg = ...
this.typeListSectionDiffAlg = ...
this.annotationSetRefListSectionDiffAlg = ...
this.annotationSetSectionDiffAlg = ...
this.classDataSectionDiffAlg = ...
this.codeSectionDiffAlg = ...
this.debugInfoSectionDiffAlg = ...
this.annotationSectionDiffAlg = ...
this.encodedArraySectionDiffAlg = ...
this.annotationsDirectorySectionDiffAlg = ...
}看到其首先为oldDex,newDex赋值,然后依次初始化了15个算法,每个算法代表每个区域,算法的目的就像我们之前描述的那样,要知道“删除了哪些,新增了哪些”;
我们继续看代码:
dexPatchGenerator.executeAndSaveTo(patchFile);
有了dexPatchGenerator对象后,直接指向了executeAndSaveTo方法。
public void executeAndSaveTo(File file) throws IOException {
OutputStream os = null;
try {
os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
executeAndSaveTo(os);
} finally {
if (os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// ignored.
}
}
}
}到executeAndSaveTo方法:
public void executeAndSaveTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
int patchedheaderSize = SizeOf.HEADER_ITEM;
int patchedStringIdsSize = newDex.getTableOfContents().stringIds.size * SizeOf.STRING_ID_ITEM;
int patchedTypeIdsSize = newDex.getTableOfContents().typeIds.size * SizeOf.TYPE_ID_ITEM;
int patchedProtoIdsSize = newDex.getTableOfContents().protoIds.size * SizeOf.PROTO_ID_ITEM;
int patchedFieldIdsSize = newDex.getTableOfContents().fieldIds.size * SizeOf.MEMBER_ID_ITEM;
int patchedMethodIdsSize = newDex.getTableOfContents().methodIds.size * SizeOf.MEMBER_ID_ITEM;
int patchedClassDefsSize = newDex.getTableOfContents().classDefs.size * SizeOf.CLASS_DEF_ITEM;
int patchedIdSectionSize =
patchedStringIdsSize
+ patchedTypeIdsSize
+ patchedProtoIdsSize
+ patchedFieldIdsSize
+ patchedMethodIdsSize
+ patchedClassDefsSize;
this.patchedHeaderOffset = 0;
this.patchedStringIdsOffset = patchedHeaderOffset + patchedheaderSize;
this.stringDataSectionDiffAlg.execute();
this.patchedStringDataItemsOffset = patchedheaderSize + patchedIdSectionSize;
this.stringDataSectionDiffAlg.simulatePatchOperation(this.patchedStringDataItemsOffset);
// 省略了其余14个算法的一堆代码
this.patchedDexSize
= this.patchedMapListOffset
+ patchedMapListSize;
writeResultToStream(out);
}因为涉及到15个算法,所以这里的代码非常长,我们这里只拿其中一个算法来说明。
每个算法都会执行execute和simulatePatchOperation方法:
首先看execute:
public void execute() {
this.patchOperationList.clear();
// 1. 拿到oldDex和newDex的itemList
this.adjustedOldIndexedItemsWithOrigOrder = collectSectionItems(this.oldDex, true);
this.oldItemCount = this.adjustedOldIndexedItemsWithOrigOrder.length;
AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, T>[] adjustedOldIndexedItems = new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry[this.oldItemCount];
System.arraycopy(this.adjustedOldIndexedItemsWithOrigOrder, 0, adjustedOldIndexedItems, 0, this.oldItemCount);
Arrays.sort(adjustedOldIndexedItems, this.comparatorForItemDiff);
AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, T>[] adjustedNewIndexedItems = collectSectionItems(this.newDex, false);
this.newItemCount = adjustedNewIndexedItems.length;
Arrays.sort(adjustedNewIndexedItems, this.comparatorForItemDiff);
int oldCursor = 0;
int newCursor = 0;
// 2.遍历,对比,收集patch操作
while (oldCursor < this.oldItemCount || newCursor < this.newItemCount) {
if (oldCursor >= this.oldItemCount) {
// rest item are all newItem.
while (newCursor < this.newItemCount) {
// 对剩下的newItem做ADD操作
}
} else if (newCursor >= newItemCount) {
// rest item are all oldItem.
while (oldCursor < oldItemCount) {
// 对剩下的oldItem做DEL操作
}
} else {
AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, T> oldIndexedItem = adjustedOldIndexedItems[oldCursor];
AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, T> newIndexedItem = adjustedNewIndexedItems[newCursor];
int cmpRes = oldIndexedItem.getValue().compareTo(newIndexedItem.getValue());
if (cmpRes < 0) {
int deletedIndex = oldIndexedItem.getKey();
int deletedOffset = getItemOffsetOrIndex(deletedIndex, oldIndexedItem.getValue());
this.patchOperationList.add(new PatchOperation<T>(PatchOperation.OP_DEL, deletedIndex));
markDeletedIndexOrOffset(this.oldToPatchedIndexMap, deletedIndex, deletedOffset);
++oldCursor;
} else if (cmpRes > 0) {
this.patchOperationList.add(new PatchOperation<>(PatchOperation.OP_ADD,
newIndexedItem.getKey(), newIndexedItem.getValue()));
++newCursor;
} else {
int oldIndex = oldIndexedItem.getKey();
int newIndex = newIndexedItem.getKey();
int oldOffset = getItemOffsetOrIndex(oldIndexedItem.getKey(), oldIndexedItem.getValue());
int newOffset = getItemOffsetOrIndex(newIndexedItem.getKey(), newIndexedItem.getValue());
if (oldIndex != newIndex) {
this.oldIndexToNewIndexMap.put(oldIndex, newIndex);
}
if (oldOffset != newOffset) {
this.oldOffsetToNewOffsetMap.put(oldOffset, newOffset);
}
++oldCursor;
++newCursor;
}
}
}
// 未完
}可以看到首先读取oldDex和newDex对应区域的数据并排序,分别adjustedOldIndexedItems和adjustedNewIndexedItems。
接下来就开始遍历了,直接看else部分:
分别根据当前的cursor,获取oldItem和newItem,对其value对对比:
- 如果<0 ,则认为该old Item被删除了,记录为PatchOperation.OP_DEL,并记录该oldItem index到PatchOperation对象,加入到patchOperationList中。
- 如果>0,则认为该newItem是新增的,记录为PatchOperation.OP_ADD,并记录该newItem index和value到PatchOperation对象,加入到patchOperationList中。
- 如果=0,不会生成PatchOperation。
经过上述,我们得到了一个patchOperationList对象。
继续下半部分代码:
public void execute() {
// 接上...
// 根据index排序,如果index一样,则先DEL后ADD
Collections.sort(this.patchOperationList, comparatorForPatchOperationOpt);
Iterator<PatchOperation<T>> patchOperationIt = this.patchOperationList.iterator();
PatchOperation<T> prevPatchOperation = null;
while (patchOperationIt.hasNext()) {
PatchOperation<T> patchOperation = patchOperationIt.next();
if (prevPatchOperation != null
&& prevPatchOperation.op == PatchOperation.OP_DEL
&& patchOperation.op == PatchOperation.OP_ADD
) {
if (prevPatchOperation.index == patchOperation.index) {
prevPatchOperation.op = PatchOperation.OP_REPLACE;
prevPatchOperation.newItem = patchOperation.newItem;
patchOperationIt.remove();
prevPatchOperation = null;
} else {
prevPatchOperation = patchOperation;
}
} else {
prevPatchOperation = patchOperation;
}
}
// Finally we record some information for the final calculations.
patchOperationIt = this.patchOperationList.iterator();
while (patchOperationIt.hasNext()) {
PatchOperation<T> patchOperation = patchOperationIt.next();
switch (patchOperation.op) {
case PatchOperation.OP_DEL: {
indexToDelOperationMap.put(patchOperation.index, patchOperation);
break;
}
case PatchOperation.OP_ADD: {
indexToAddOperationMap.put(patchOperation.index, patchOperation);
break;
}
case PatchOperation.OP_REPLACE: {
indexToReplaceOperationMap.put(patchOperation.index, patchOperation);
break;
}
}
}
}- 首先对patchOperationList按照index排序,如果index一致则先DEL、后ADD。
- 接下来一个对所有的operation的迭代,主要将index一致的,且连续的DEL、ADD转化为REPLACE操作。
- 最后将patchOperationList转化为3个Map,分别为:indexToDelOperationMap,indexToAddOperationMap,indexToReplaceOperationMap。
ok,经历完成execute之后,我们主要的产物就是3个Map,分别记录了:oldDex中哪些index需要删除;newDex中新增了哪些item;哪些item需要替换为新item。
刚才说了每个算法除了execute()还有个simulatePatchOperation()
this.stringDataSectionDiffAlg
.simulatePatchOperation(this.patchedStringDataItemsOffset);传入的偏移量为data区域的偏移量。
public void simulatePatchOperation(int baseOffset) {
int oldIndex = 0;
int patchedIndex = 0;
int patchedOffset = baseOffset;
while (oldIndex < this.oldItemCount || patchedIndex < this.newItemCount) {
if (this.indexToAddOperationMap.containsKey(patchedIndex)) {
//省略了一些代码
T newItem = patchOperation.newItem;
int itemSize = getItemSize(newItem);
++patchedIndex;
patchedOffset += itemSize;
} else if (this.indexToReplaceOperationMap.containsKey(patchedIndex)) {
//省略了一些代码
T newItem = patchOperation.newItem;
int itemSize = getItemSize(newItem);
++patchedIndex;
patchedOffset += itemSize;
} else if (this.indexToDelOperationMap.containsKey(oldIndex)) {
++oldIndex;
} else if (this.indexToReplaceOperationMap.containsKey(oldIndex)) {
++oldIndex;
} else if (oldIndex < this.oldItemCount) {
++oldIndex;
++patchedIndex;
patchedOffset += itemSize;
}
}
this.patchedSectionSize = SizeOf.roundToTimesOfFour(patchedOffset - baseOffset);
}遍历oldIndex与newIndex,分别在indexToAddOperationMap,indexToReplaceOperationMap,indexToDelOperationMap中查找。
这里关注一点最终的一个产物是this.patchedSectionSize,由patchedOffset-baseOffset所得。
这里有几种情况会造成patchedOffset+=itemSize:
- indexToAddOperationMap中包含patchIndex
- indexToReplaceOperationMap包含patchIndex
- 不在indexToDelOperationMap与indexToReplaceOperationMap中的oldDex.
其实很好理解,这个patchedSectionSize其实对应newDex的这个区域的size。所以,包含需要ADD的Item,会被替代的Item,以及OLD ITEMS中没有被删除和替代的Item。这三者相加即为newDex的itemList。
到这里,一个算法就执行完毕了。
经过这样的一个算法,我们得到了PatchOperationList和对应区域sectionSize。那么执行完成所有的算法,应该会得到针对每个算法的PatchOperationList,和每个区域的sectionSize;每个区域的sectionSize实际上换算得到每个区域的offset。
每个区域的算法,execute和simulatePatchOperation代码都是复用的,所以其他的都只有细微的变化,可以自己看了。
接下来看执行完成所有的算法后的writeResultToStream方法。
private void writeResultToStream(OutputStream os) throws IOException {
DexDataBuffer buffer = new DexDataBuffer();
buffer.write(DexPatchFile.MAGIC); // DEXDIFF
buffer.writeShort(DexPatchFile.CURRENT_VERSION); /0x0002
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedDexSize);
// we will return here to write firstChunkOffset later.
int posOfFirstChunkOffsetField = buffer.position();
buffer.writeInt(0);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedStringIdsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedTypeIdsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedProtoIdsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedFieldIdsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedMethodIdsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedClassDefsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedMapListOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedTypeListsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedAnnotationSetRefListItemsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedAnnotationSetItemsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedClassDataItemsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedCodeItemsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedStringDataItemsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedDebugInfoItemsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedAnnotationItemsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedEncodedArrayItemsOffset);
buffer.writeInt(this.patchedAnnotationsDirectoryItemsOffset);
buffer.write(this.oldDex.computeSignature(false));
int firstChunkOffset = buffer.position();
buffer.position(posOfFirstChunkOffsetField);
buffer.writeInt(firstChunkOffset);
buffer.position(firstChunkOffset);
writePatchOperations(buffer, this.stringDataSectionDiffAlg.getPatchOperationList());
// 省略其他14个writePatch...
byte[] bufferData = buffer.array();
os.write(bufferData);
os.flush();
}- 首先写了MAGIC,CURRENT_VERSION主要用于检查该文件为合法的tinker patch 文件。
- 然后写入patchedDexSize
- 第四位写入的是数据区的offset,可以看到先使用0站位,等所有的map list相关的offset书写结束,写入当前的位置。
- 接下来写入所有的跟maplist各个区域相关的offset(这里各个区域的排序不重要,读写一致即可)
- 然后执行每个算法写入对应区域的信息
- 最后生成patch文件
我们依旧只看stringDataSectionDiffAlg这个算法。
private <T extends Comparable<T>> void writePatchOperations(
DexDataBuffer buffer, List<PatchOperation<T>> patchOperationList
) {
List<Integer> delOpIndexList = new ArrayList<>(patchOperationList.size());
List<Integer> addOpIndexList = new ArrayList<>(patchOperationList.size());
List<Integer> replaceOpIndexList = new ArrayList<>(patchOperationList.size());
List<T> newItemList = new ArrayList<>(patchOperationList.size());
for (PatchOperation<T> patchOperation : patchOperationList) {
switch (patchOperation.op) {
case PatchOperation.OP_DEL: {
delOpIndexList.add(patchOperation.index);
break;
}
case PatchOperation.OP_ADD: {
addOpIndexList.add(patchOperation.index);
newItemList.add(patchOperation.newItem);
break;
}
case PatchOperation.OP_REPLACE: {
replaceOpIndexList.add(patchOperation.index);
newItemList.add(patchOperation.newItem);
break;
}
}
}
buffer.writeUleb128(delOpIndexList.size());
int lastIndex = 0;
for (Integer index : delOpIndexList) {
buffer.writeSleb128(index - lastIndex);
lastIndex = index;
}
buffer.writeUleb128(addOpIndexList.size());
lastIndex = 0;
for (Integer index : addOpIndexList) {
buffer.writeSleb128(index - lastIndex);
lastIndex = index;
}
buffer.writeUleb128(replaceOpIndexList.size());
lastIndex = 0;
for (Integer index : replaceOpIndexList) {
buffer.writeSleb128(index - lastIndex);
lastIndex = index;
}
for (T newItem : newItemList) {
if (newItem instanceof StringData) {
buffer.writeStringData((StringData) newItem);
}
// else 其他类型,write其他类型Data
}
}首先将我们的patchOperationList转化为3个OpIndexList,分别对应DEL,ADD,REPLACE,以及将所有的item存入newItemList。
然后依次写入:
- del操作的个数,每个del的index
- add操作的个数,每个add的index
- replace操作的个数,每个需要replace的index
- 最后依次写入newItemList.
这里index都做了(这里做了个index – lastIndex操作)
其他的算法也是执行了类似的操作。
最好来看看我们生成的patch是什么样子的:
- 首先包含几个字段,证明自己是tinker patch
- 包含生成newDex各个区域的offset,即可以将newDex划分了多个区域,定位到起点
- 包含newDex各个区域的Item的删除的索引(oldDex),新增的索引和值,替换的索引和值
那么这么看,我们猜测Patch的逻辑时这样的:
- 首先根据各个区域的offset,确定各个区域的起点
- 读取oldDex各个区域的items,然后根据patch中去除掉oldDex中需要删除的和需要替换的item,再加上新增的item和替换的item即可组成newOld该区域的items。
即,newDex的某个区域的包含:
oldItems - del - replace + addItems + replaceItems
这么看挺清晰的,下面看代码咯~
与diff一样,肯定有那么一个类或者方法,接受old dex File 和 patch File,最后生成new Dex。不要陷在一堆安全校验,apk解压的代码中。
这个类叫做DexPatchApplier,在tinker-commons中。
patch的相关代码如下:
@Test
public void testPatch() throws IOException {
File oldFile = new File("Hello.dex");
File patchFile = new File("patch.dex");
File newFile = new File("new.dex");
DexPatchApplier dexPatchGenerator
= new DexPatchApplier(oldFile, patchFile);
dexPatchGenerator.executeAndSaveTo(newFile);
}可以看到和diff代码类似,下面看代码去。
public DexPatchApplier(File oldDexIn, File patchFileIn) throws IOException {
this(new Dex(oldDexIn), new DexPatchFile(patchFileIn));
}oldDex会转化为Dex对象,这个上面分析过,主要就是readHeader和readMap.注意我们的patchFile是转为一个DexPatchFile对象。
public DexPatchFile(File file) throws IOException {
this.buffer = new DexDataBuffer(ByteBuffer.wrap(FileUtils.readFile(file)));
init();
}首先将patch file读取为byte[],然后调用init
private void init() {
byte[] magic = this.buffer.readByteArray(MAGIC.length);
if (CompareUtils.uArrCompare(magic, MAGIC) != 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("bad dex patch file magic: " + Arrays.toString(magic));
}
this.version = this.buffer.readShort();
if (CompareUtils.uCompare(this.version, CURRENT_VERSION) != 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("bad dex patch file version: " + this.version + ", expected: " + CURRENT_VERSION);
}
this.patchedDexSize = this.buffer.readInt();
this.firstChunkOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedStringIdSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedTypeIdSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedProtoIdSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedFieldIdSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedMethodIdSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedClassDefSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedMapListSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedTypeListSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedAnnotationSetRefListSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedAnnotationSetSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedClassDataSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedCodeSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedStringDataSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedDebugInfoSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedAnnotationSectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedEncodedArraySectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.patchedAnnotationsDirectorySectionOffset = this.buffer.readInt();
this.oldDexSignature = this.buffer.readByteArray(SizeOf.SIGNATURE);
this.buffer.position(firstChunkOffset);
}还记得我们写patch的操作么,先写了MAGIC和Version用于校验该文件是一个patch file;接下来为patchedDexSize和各种offset进行赋值;最后定位到数据区(firstChunkOffset),还记得写的时候,该字段在第四个位置。
定位到该位置后,后面读取的就是数据了,数据存的时候按照如下格式存储的:
- del操作的个数,每个del的index
- add操作的个数,每个add的index
- replace操作的个数,每个需要replace的index
- 最后依次写入newItemList.
简单回忆下,我们继续源码分析。
public DexPatchApplier(File oldDexIn, File patchFileIn) throws IOException {
this(new Dex(oldDexIn), new DexPatchFile(patchFileIn));
}
public DexPatchApplier(
Dex oldDexIn,
DexPatchFile patchFileIn) {
this.oldDex = oldDexIn;
this.patchFile = patchFileIn;
this.patchedDex = new Dex(patchFileIn.getPatchedDexSize());
this.oldToPatchedIndexMap = new SparseIndexMap();
}除了oldDex,patchFile,还初始化了一个patchedDex作为我们最终输出Dex对象。
构造完成后,直接执行了executeAndSaveTo方法。
public void executeAndSaveTo(File file) throws IOException {
OutputStream os = null;
try {
os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
executeAndSaveTo(os);
} finally {
if (os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// ignored.
}
}
}
}直接到executeAndSaveTo(os),该方法代码比较长,我们分3段讲解:
public void executeAndSaveTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
TableOfContents patchedToc = this.patchedDex.getTableOfContents();
patchedToc.header.off = 0;
patchedToc.header.size = 1;
patchedToc.mapList.size = 1;
patchedToc.stringIds.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedStringIdSectionOffset();
patchedToc.typeIds.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedTypeIdSectionOffset();
patchedToc.typeLists.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedTypeListSectionOffset();
patchedToc.protoIds.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedProtoIdSectionOffset();
patchedToc.fieldIds.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedFieldIdSectionOffset();
patchedToc.methodIds.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedMethodIdSectionOffset();
patchedToc.classDefs.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedClassDefSectionOffset();
patchedToc.mapList.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedMapListSectionOffset();
patchedToc.stringDatas.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedStringDataSectionOffset();
patchedToc.annotations.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedAnnotationSectionOffset();
patchedToc.annotationSets.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedAnnotationSetSectionOffset();
patchedToc.annotationSetRefLists.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedAnnotationSetRefListSectionOffset();
patchedToc.annotationsDirectories.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedAnnotationsDirectorySectionOffset();
patchedToc.encodedArrays.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedEncodedArraySectionOffset();
patchedToc.debugInfos.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedDebugInfoSectionOffset();
patchedToc.codes.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedCodeSectionOffset();
patchedToc.classDatas.off
= this.patchFile.getPatchedClassDataSectionOffset();
patchedToc.fileSize
= this.patchFile.getPatchedDexSize();
Arrays.sort(patchedToc.sections);
patchedToc.computeSizesFromOffsets();
// 未完待续...
}这里实际上,就是读取patchFile中记录的值给patchedDex的TableOfContent中各种Section(大致对应map list中各个map_list_item)赋值。
接下来排序呢,设置byteCount等字段信息。
继续:
public void executeAndSaveTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
// 省略第一部分代码
// Secondly, run patch algorithms according to sections' dependencies.
this.stringDataSectionPatchAlg = new StringDataSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.typeIdSectionPatchAlg = new TypeIdSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.protoIdSectionPatchAlg = new ProtoIdSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.fieldIdSectionPatchAlg = new FieldIdSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.methodIdSectionPatchAlg = new MethodIdSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.classDefSectionPatchAlg = new ClassDefSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.typeListSectionPatchAlg = new TypeListSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.annotationSetRefListSectionPatchAlg = new AnnotationSetRefListSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.annotationSetSectionPatchAlg = new AnnotationSetSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.classDataSectionPatchAlg = new ClassDataSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.codeSectionPatchAlg = new CodeSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.debugInfoSectionPatchAlg = new DebugInfoItemSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.annotationSectionPatchAlg = new AnnotationSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.encodedArraySectionPatchAlg = new StaticValueSectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.annotationsDirectorySectionPatchAlg = new AnnotationsDirectorySectionPatchAlgorithm(
patchFile, oldDex, patchedDex, oldToPatchedIndexMap
);
this.stringDataSectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.typeIdSectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.typeListSectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.protoIdSectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.fieldIdSectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.methodIdSectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.annotationSectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.annotationSetSectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.annotationSetRefListSectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.annotationsDirectorySectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.debugInfoSectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.codeSectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.classDataSectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.encodedArraySectionPatchAlg.execute();
this.classDefSectionPatchAlg.execute();
//未完待续...
}这一部分很明显初始化了一堆算法,然后分别去执行。我们依然是拿stringDataSectionPatchAlg来分析。
public void execute() {
final int deletedItemCount = patchFile.getBuffer().readUleb128();
final int[] deletedIndices = readDeltaIndiciesOrOffsets(deletedItemCount);
final int addedItemCount = patchFile.getBuffer().readUleb128();
final int[] addedIndices = readDeltaIndiciesOrOffsets(addedItemCount);
final int replacedItemCount = patchFile.getBuffer().readUleb128();
final int[] replacedIndices = readDeltaIndiciesOrOffsets(replacedItemCount);
final TableOfContents.Section tocSec = getTocSection(this.oldDex);
Dex.Section oldSection = null;
int oldItemCount = 0;
if (tocSec.exists()) {
oldSection = this.oldDex.openSection(tocSec);
oldItemCount = tocSec.size;
}
// Now rest data are added and replaced items arranged in the order of
// added indices and replaced indices.
doFullPatch(
oldSection, oldItemCount, deletedIndices, addedIndices, replacedIndices
);
}再贴一下我们写入时的规则:
- del操作的个数,每个del的index
- add操作的个数,每个add的index
- replace操作的个数,每个需要replace的index
- 最后依次写入newItemList.
看代码,读取顺序如下:
- del的数量,del的所有的index存储在一个int[]中;
- add的数量,add的所有的index存储在一个int[]中;
- replace的数量,replace的所有的index存储在一个int[]中;
是不是和写入时一致。
继续,接下来获取了oldDex中oldItems和oldItemCount。
那么现在有了:
- del count and indices
- add count add indices
- replace count and indices
- oldItems and oldItemCount
拿着我们拥有的,继续执行doFullPatch
private void doFullPatch(
Dex.Section oldSection,
int oldItemCount,
int[] deletedIndices,
int[] addedIndices,
int[] replacedIndices) {
int deletedItemCount = deletedIndices.length;
int addedItemCount = addedIndices.length;
int replacedItemCount = replacedIndices.length;
int newItemCount = oldItemCount + addedItemCount - deletedItemCount;
int deletedItemCounter = 0;
int addActionCursor = 0;
int replaceActionCursor = 0;
int oldIndex = 0;
int patchedIndex = 0;
while (oldIndex < oldItemCount || patchedIndex < newItemCount) {
if (addActionCursor < addedItemCount && addedIndices[addActionCursor] == patchedIndex) {
T addedItem = nextItem(patchFile.getBuffer());
int patchedOffset = writePatchedItem(addedItem);
++addActionCursor;
++patchedIndex;
} else
if (replaceActionCursor < replacedItemCount && replacedIndices[replaceActionCursor] == patchedIndex) {
T replacedItem = nextItem(patchFile.getBuffer());
int patchedOffset = writePatchedItem(replacedItem);
++replaceActionCursor;
++patchedIndex;
} else
if (Arrays.binarySearch(deletedIndices, oldIndex) >= 0) {
T skippedOldItem = nextItem(oldSection); // skip old item.
++oldIndex;
++deletedItemCounter;
} else
if (Arrays.binarySearch(replacedIndices, oldIndex) >= 0) {
T skippedOldItem = nextItem(oldSection); // skip old item.
++oldIndex;
} else
if (oldIndex < oldItemCount) {
T oldItem = adjustItem(this.oldToPatchedIndexMap, nextItem(oldSection));
int patchedOffset = writePatchedItem(oldItem);
++oldIndex;
++patchedIndex;
}
}
}先整体上看一下,这里的目的就是往patchedDex的stringData区写数据,写的数据理论上应该是:
- 新增的数据
- 替代的数据
- oldDex中出去新增和被替代的数据
当然他们需要顺序写入。
所以看代码,首先计算出newItemCount=oldItemCount + addCount - delCount,然后开始遍历,遍历条件为0~oldItemCount或0~newItemCount。
我们期望的是,在patchIndex从0~newItemCount之间都会写入对应的Item。
Item写入通过代码我们可以看到:
- 首先判断该patchIndex是否包含在addIndices中,如果包含则写入;
- 再者判断是否在repalceIndices中,如果包含则写入;
- 然后判断如果发现oldIndex被delete或者replace,直接跳过;
- 那么最后一个index指的就是,oldIndex为非delete和replace的,也就是和newDex中items相同的部分。
上述1.2.4三个部分即可组成完整的newDex的该区域。
这样的话就完成了stringData区域的patch算法。
其他剩下的14个算法的execute代码是相同的(父类),执行的操作类似,都会完成各个部分的patch算法。
当所有的区域都完成恢复后,那么剩下的就是header和mapList了,所以回到所有算法执行完成的地方:
public void executeAndSaveTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
//1.省略了offset的各种赋值
//2.省略了各个部分的patch算法
// Thirdly, write header, mapList. Calculate and write patched dex's sign and checksum.
Dex.Section headerOut = this.patchedDex.openSection(patchedToc.header.off);
patchedToc.writeHeader(headerOut);
Dex.Section mapListOut = this.patchedDex.openSection(patchedToc.mapList.off);
patchedToc.writeMap(mapListOut);
this.patchedDex.writeHashes();
// Finally, write patched dex to file.
this.patchedDex.writeTo(out);
}定位到header区域,写header相关数据;定位到map list区域,编写map list相关数据。两者都完成的时候,需要编写header中比较特殊的两个字段:签名和checkSum,因为这两个字段是依赖map list的,所以必须在编写map list后。
这样就完成了完整的dex的恢复,最后将内存中的所有数据写到文件中。
刚才我们有个Hello.dex,我们再编写一个类:
public class World{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("nani World");
}
}然后将这个类编译以及打成dx文件。
javac -source 1.7 -target 1.7 World.java dx --dex --output=World.dex World.class
这样我们就准备好了两个dex,Hello.dex和World.dex.
使用010 Editor分别打开两个dex,我们主要关注string_id_item;
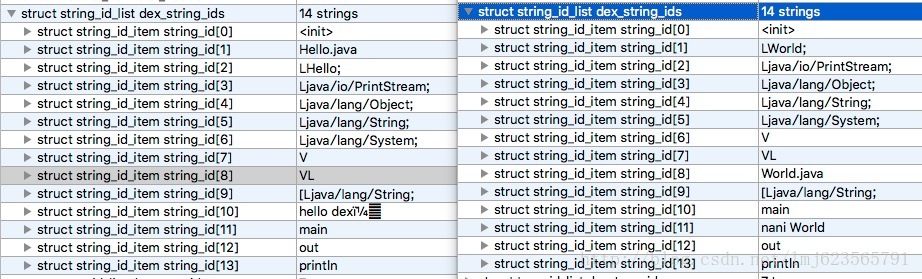
两边分别13个字符串,按照我们上面介绍的diff算法,我们可以得到以下操作:
两边的字符串分别开始遍历对比:
- 如果<0 ,则认为该old Item被删除了,记录为PatchOperation.OP_DEL,并记录该oldItem index到PatchOperation对象,加入到patchOperationList中。
- 如果>0,则认为该newItem是新增的,记录为PatchOperation.OP_ADD,并记录该newItem index和value到PatchOperation对象,加入到patchOperationList中。
- 如果=0,不会生成PatchOperation。
del 1 add 1 LWorld; del 2 add 8 World.java del 10 add 11 naniWorld
然后是根据索引排序,没有变化;
接下来遍历所有的操作,将index一致且DEL和ADD相邻的操作替换为replace
replace 1 LWorld del 2 add 8 World.java del 10 add 11 naniWorld
最终在write时,会做一次遍历,将操作按DEL,ADD,REPLACE进行分类,并且将出现的item放置到newItemList中。
del ops:
del 2
del 10
add ops:
add 8
add 11
replace ops:
replace 1newItemList变为:
LWorld //replace 1 World.java //add 8 naniWorld //add 11
然后写入,那么写入的顺序应该是:
2 //del size 2 8 // index - lastIndex 2 // add size 8 3 // index - lastIndex 1 //replace size 1 LWorld World.java naniWorld
这里我们直接在DexPatchGenerator的writeResultToStream的相关位置打上日志:
buffer.writeUleb128(delOpIndexList.size());
System.out.println("del size = " + delOpIndexList.size());
int lastIndex = 0;
for (Integer index : delOpIndexList) {
buffer.writeSleb128(index - lastIndex);
System.out.println("del index = " + (index - lastIndex));
lastIndex = index;
}
buffer.writeUleb128(addOpIndexList.size());
System.out.println("add size = " + addOpIndexList.size());
lastIndex = 0;
for (Integer index : addOpIndexList) {
buffer.writeSleb128(index - lastIndex);
System.out.println("add index = " + (index - lastIndex));
lastIndex = index;
}
buffer.writeUleb128(replaceOpIndexList.size());
System.out.println("replace size = " + addOpIndexList.size());
lastIndex = 0;
for (Integer index : replaceOpIndexList) {
buffer.writeSleb128(index - lastIndex);
System.out.println("replace index = " + (index - lastIndex));
lastIndex = index;
}
for (T newItem : newItemList) {
if (newItem instanceof StringData) {
buffer.writeStringData((StringData) newItem);
System.out.println("stringdata = " + ((StringData) newItem).value);
}
}可以看到输出为:
del size = 2 del index = 2 del index = 8 add size = 2 add index = 8 add index = 3 replace size = 2 replace index = 1 stringdata = LWorld; stringdata = World.java stringdata = nani World
与我们上述分析结果一致 ~~
那么其他区域可以用类似的方式去验证,patch的话也差不多,就不赘述了。
以上是Android 热修复 Tinker 源码分析的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

热门话题
 centos和ubuntu的区别
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
centos和ubuntu的区别
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
CentOS 和 Ubuntu 的关键差异在于:起源(CentOS 源自 Red Hat,面向企业;Ubuntu 源自 Debian,面向个人)、包管理(CentOS 使用 yum,注重稳定;Ubuntu 使用 apt,更新频率高)、支持周期(CentOS 提供 10 年支持,Ubuntu 提供 5 年 LTS 支持)、社区支持(CentOS 侧重稳定,Ubuntu 提供广泛教程和文档)、用途(CentOS 偏向服务器,Ubuntu 适用于服务器和桌面),其他差异包括安装精简度(CentOS 精
 centos如何安装
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
centos如何安装
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
CentOS 安装步骤:下载 ISO 映像并刻录可引导媒体;启动并选择安装源;选择语言和键盘布局;配置网络;分区硬盘;设置系统时钟;创建 root 用户;选择软件包;开始安装;安装完成后重启并从硬盘启动。
 Centos停止维护后的选择
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
Centos停止维护后的选择
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
CentOS 已停止维护,替代选择包括:1. Rocky Linux(兼容性最佳);2. AlmaLinux(与 CentOS 兼容);3. Ubuntu Server(需要配置);4. Red Hat Enterprise Linux(商业版,付费许可);5. Oracle Linux(与 CentOS 和 RHEL 兼容)。在迁移时,考虑因素有:兼容性、可用性、支持、成本和社区支持。
 docker desktop怎么用
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
docker desktop怎么用
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
如何使用 Docker Desktop?Docker Desktop 是一款工具,用于在本地机器上运行 Docker 容器。其使用步骤包括:1. 安装 Docker Desktop;2. 启动 Docker Desktop;3. 创建 Docker 镜像(使用 Dockerfile);4. 构建 Docker 镜像(使用 docker build);5. 运行 Docker 容器(使用 docker run)。
 docker原理详解
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
docker原理详解
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker利用Linux内核特性,提供高效、隔离的应用运行环境。其工作原理如下:1. 镜像作为只读模板,包含运行应用所需的一切;2. 联合文件系统(UnionFS)层叠多个文件系统,只存储差异部分,节省空间并加快速度;3. 守护进程管理镜像和容器,客户端用于交互;4. Namespaces和cgroups实现容器隔离和资源限制;5. 多种网络模式支持容器互联。理解这些核心概念,才能更好地利用Docker。
 docker镜像失败怎么办
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
docker镜像失败怎么办
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Docker镜像构建失败的故障排除步骤:检查Dockerfile语法和依赖项版本。检查构建上下文中是否包含所需源代码和依赖项。查看构建日志以获取错误详细信息。使用--target选项构建分层阶段以识别失败点。确保使用最新版本的Docker引擎。使用--t [image-name]:debug模式构建镜像以调试问题。检查磁盘空间并确保足够。禁用SELinux以防止干扰构建过程。向社区平台寻求帮助,提供Dockerfile和构建日志描述以获得更具体的建议。
 vscode需要什么电脑配置
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
vscode需要什么电脑配置
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code 系统要求:操作系统:Windows 10 及以上、macOS 10.12 及以上、Linux 发行版处理器:最低 1.6 GHz,推荐 2.0 GHz 及以上内存:最低 512 MB,推荐 4 GB 及以上存储空间:最低 250 MB,推荐 1 GB 及以上其他要求:稳定网络连接,Xorg/Wayland(Linux)
 Docker使用了哪些底层技术?
Apr 15, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Docker使用了哪些底层技术?
Apr 15, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Docker 使用容器引擎、镜像格式、存储驱动程序、网络模型、容器编排工具、操作系统虚拟化和容器注册表等技术来支持其容器化功能,提供轻量级、可移植且自动化的应用程序部署和管理。






