这篇文章主要介绍了javabean四个作用域范围的详解的相关资料,希望通过本文能帮助到大家,需要的朋友可以参考下
JavaBean四个作用域范围的详解
一 说明
使用useBeans的scope属性可以用来指定javabean的作用范围。
二 四个作用范围
立即学习“Java免费学习笔记(深入)”;

三 代码
1、login.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" %>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >
<title>My JSP 'login.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>系统登录</h1>
<hr>
<form name="loginForm" action="dologin.jsp?mypass=999999" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>用户名:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="username" value=""/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密码:</td>
<td><input type="password" name="password" value=""/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" align="center"><input type="submit" value="登录"/></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>2、dologin.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >
<title>My JSP 'dologin.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >
-->
</head>
<body>
<jsp:useBean id="myUsers" class="com.po.Users" scope="page"/>
<h1>setProperty动作元素</h1>
<hr>
<!--根据表单自动匹配所有的属性 -->
<%--
<jsp:setProperty name="myUsers" property="*"/>
--%>
<!--根据表单匹配所有部分的属性 -->
<%--
<jsp:setProperty name="myUsers" property="username"/>
--%>
<!--根表单无关,通过手工赋值给属性 -->
<%--
<jsp:setProperty name="myUsers" property="username" value="lisi"/>
<jsp:setProperty name="myUsers" property="password" value="888888"/>
--%>
<!--通过URL传参数给属性赋值 -->
<jsp:setProperty name="myUsers" property="username"/>
<jsp:setProperty name="myUsers" property="password" param="mypass"/>
<!-- 使用传统的表达式方式来获取用户名和密码 -->
<%--
用户名:<%=myUsers.getUsername() %><br>
密码:<%=myUsers.getPassword() %><br>
--%>
<!-- 使用getProperty方式来获取用户名和密码 -->
用户名:<jsp:getProperty name="myUsers" property="username"/> <br>
密码:<jsp:getProperty name="myUsers" property="password"/><br>
<br>
<br>
<a href="testScope.jsp" rel="external nofollow" >测试javabean的四个作用域范围</a>
<%
request.getRequestDispatcher("testScope.jsp").forward(request, response);
%>
</body>
</html>3、testScope.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*"
contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"%>
<%@ page import="com.po.Users"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://"
+ request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort()
+ path + "/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >
<title>My JSP 'testScope.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>Javabean的四个作用域范围</h1>
<hr>
<jsp:useBean id="myUsers" class="com.po.Users" scope="page" />
用户名:<jsp:getProperty name="myUsers" property="username" /><br> 密码:<jsp:getProperty
name="myUsers" property="password" /><br>
<!-- 使用内置对象获取用户名和密码 -->
<hr>
<%--
用户名:<%=((Users)application.getAttribute("myUsers")).getUsername()%><br>
密码:<%=((Users)application.getAttribute("myUsers")).getPassword() %><br>
--%>
<%--
用户名:<%=((Users)session.getAttribute("myUsers")).getUsername()%><br>
密码:<%=((Users)session.getAttribute("myUsers")).getPassword() %><br>
--%>
<%--
用户名:<%=((Users)request.getAttribute("myUsers")).getUsername()%><br>
密码:<%=((Users)request.getAttribute("myUsers")).getPassword() %><br>
--%>
<%
String username = "";
String password = "";
if (pageContext.getAttribute("myUsers") != null) {
username = ((Users) pageContext.getAttribute("myUsers"))
.getUsername();
password = ((Users) pageContext.getAttribute("myUsers"))
.getPassword();
}
%>
用户名:<%=username%><br> 密码:<%=password%><br>
</body>
</html>四 测试结果
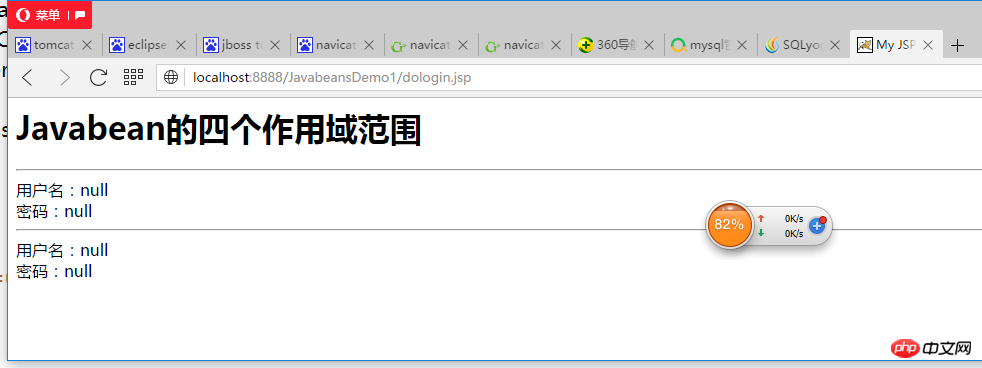
以上就是JavaBean中关于四个作用域范围的详解的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

java怎么学习?java怎么入门?java在哪学?java怎么学才快?不用担心,这里为大家提供了java速学教程(入门到精通),有需要的小伙伴保存下载就能学习啦!

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号